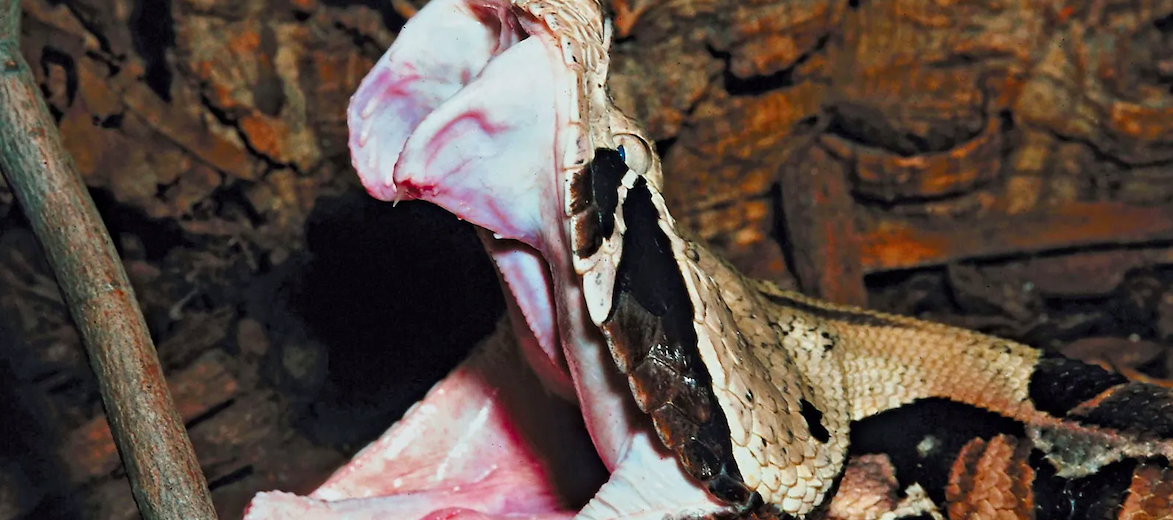
The gaboon viper touts the longest fangs and among the greatest venom yield of any known snake in the world. They are also the largest known member of the Bitis genus. Found from western to central to eastern Africa, these snakes prefer rainforests and savannas. Due to habitat loss, vehicle strike (being hit by vehicles, on roads), hunting, and trapping, these vipers are listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN.
First the Stats…
Scientific name: Bitis gabonica
Weight: Up to 35 lbs.
Length: Up to 6 feet
Lifespan: Up to 18 years
Now on to the Facts!
1.) Like other snakes, gaboons are solitary. They only come together to mate.
2.) These vipers are nocturnal (active at night).
3.) The gaboon viper is known for being generally slow moving and almost motionless for long periods of time.
4.) Not that I recommend it – EVER – but these snakes are actually tolerant of being handled and rarely bite or even emit an occasional hiss. But when they do bite, look out!
5.) Their locomotion is via a rectilinear fashion, that almost resembles walking with the ventral scales.
But wait, there’s more on the gaboon viper!
6.) Even though, as mentioned, they are hesitant to strike, when they do they are among the fastest striking snakes known.
7.) A group of vipers is called a bed, den, knot, nest, or pit.
Did you know…?
Their cytotoxic venom, that is dosed from massive venom glands, attacks cells. The symptoms of a bite can include: intense pain, rapid & conspicuous swelling, severe shock, local blistering, uncoordinated movements, defecation, urination, swelling of the eyelids & tongue, convulsions, and unconsciousness. In worst case scenarios… death.
8.) Gaboon vipers prey on mice, rats, rabbits, hares, and birds.
9.) Breeding takes place from September – December.
10.) Males battle for breeding rights by intertwining, constricting, and pushing 1 another over. They will also strike at each other with closed mouths. The winner of the battle pushes the other’s head to the ground and raises his head over the loser.
But wait, there’s still more on the gaboon viper!
11.) Females birth up to 50 live young, after up to a 7 month gestation (pregnancy).
12.) A yield of 35+ mg is enough to kill a 150 lbs. human.
13.) When a gaboon bites a victim or prey, they tend to hold on, allowing for the administering of more venom.
Now a Short Gaboon Viper Video!
Be sure to share & comment below! Also, check out the Critter Science YouTube channel. Videos added frequently!
Want to suggest a critter for me to write about? Let me know here.



